
This is a configurable flow accelerator for moving common network flow processes into hardware we believe the company is using a P4 processor. Next, some logic was mixed in to offload encryption at up to 90 Gb/s as well as offloads for storage processing like erasure coding and RAID.įinally, Broadcom added its somewhat mysterious TruFlow technology. Also, Stingray can be configured with up to 16 GB of DDR4 memory. At 3 GHz, these may be the fastest SmartNIC Arm cores. Then eight Arm v8 A72 cores clocked at 3 GHz were laid down in a cluster configuration. Single-chip SmartNIC solutions are always less costly to produce at the board level than many chip boards by other competitors.īroadcom designed the NetXtreme-S BCM58800 chip at the heart of Stingray by starting with the logic from its NetXtreme E-series controller as a base.
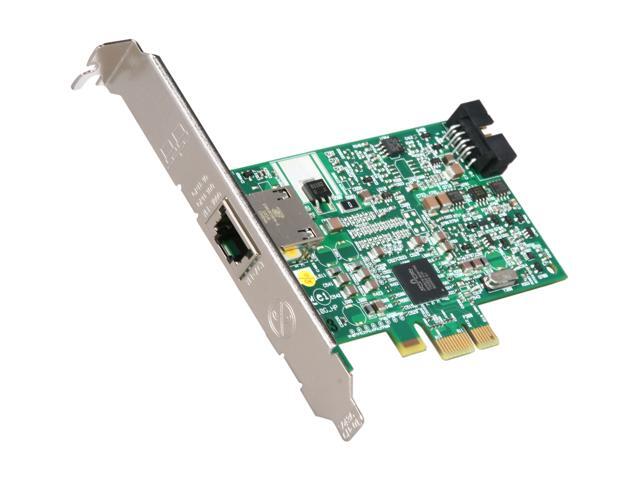

So, when it came time to assemble its Stingray SmartNIC and enter the fray, the company went with a single-chip approach (Fig. We’ll also throw in some insights on a stealth project currently called Fungible.īroadcom is the undisputed leader in the commodity Ethernet NIC controller market. The six companies selected are Broadcom, Intel, Nvidia (previously Mellanox), Netronome, Pensando, and Xilinx. To understand how SmartNICs differ from Generic NICs, let’s take a dive into the leading SmartNIC products from four of the biggest NIC companies on the planet, and two upstarts to see what improvements they offer. And on their own, they don’t generally add value to the feature set offered by that SmartNIC. Beyond architectural sketches, we won’t call out these control-plane Arm cores below, as they’re required plumbing. They don’t touch any of the network packets, and they often run “out-of-band,” meaning that they can’t be accessed via “normal” network interfaces or PCIe commands.Īlso, the cores should only accept duly signed firmware bundles over previously secured interfaces.
#BROADCOM ETHERNET CONTROLLER STATISTICS CODE#
These Arm cores typically handle loading code into the other processing elements, gathering statistics and logs, and watching over the health and configuration of the SmartNIC. Some even allow for loading a modified Linux kernel into one or more of these cores. Many of these SmartNICs will often use one or more Arm cores for control-plane management within the NIC. Field-programmable gate array (FPGA), programable logic.Flow processing cores (FPCs), which are custom-designed network processors, often P4.Collection of many Arm cores some call it clustering, others use the term grid or tiles.Then one of three approaches below are used to make an otherwise generic NIC smart by increasing its computational power through the addition of a:

Most SmartNIC approaches start with a foundational Ethernet controller either on the chip in silicon, as firmware, or as a separate chip on the adapter. The capability to load future code into a NIC, making it a SmartNIC, requires additional computational power and onboard memory not found in generic NICs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
